 Research topics
Research topics
We are now reseaching following topics.
The novel stepper motor using micro patterns
 The novel stepper motor using micro patterns(pdf)
The novel stepper motor using micro patterns(pdf)
A θ-Z acutuator

 A θ-Z acutuator(pdf)
A θ-Z acutuator(pdf)
Development of XYθz-3DOF planar stage controller

A surface encoder, which is composed of an optical 2-D angle sensor and an angle grid, can detect XYθz displacements. The resolution of the surface encoder is 20 nm in the XY directions and 0.2 arcsecond in the θz direction. The surface encoder integrated inside a planer stage system can detect 200 nm step motions in the XY directions and 1 arcsecond step motion in the θz direction.
 Development of the surface motor driven planar motion stage(pdf)
Development of the surface motor driven planar motion stage(pdf)
 Development of XYθz-3DOF planar stage controller(pdf)
Development of XYθz-3DOF planar stage controller(pdf)
Precision positioning of a sawyer motor

A surface encoder proposed in our laboratory is applied to a sawyer motor stage which has high speed and long stroke. A thin film-type angle grid, which is generated by a replication technique, is employed as a positioning scale. A positioning resolution of sub-nanometer is achieved by the closed-loop control using the surface encoder.
 Precision positioning of a sawyer motor(pdf)
Precision positioning of a sawyer motor(pdf)
Design of a nanomachining probe with nanometrology function

3-dimentional micro-structure is fabricated by an ultra precision lathe with assistance of a fast tool servo. An output of a force sensor in the fast tool servo is utilized as a measurement result of the machined surface profile. The surface profile with an accracy of nanometer-order can be obtained by measurement and corrective machining of the surface profile.
 Design of a nanomachining probe with nanometrology function(pdf)
Design of a nanomachining probe with nanometrology function(pdf)
A surface encoder for 5DOF position measurement

A surface encoder for 5DOF position measurement is composed of three 2D angle sensors (Probe 1, Probe 2 and Probe 3) and a 2D angel grid. Optical probe diameter of Probe 1 and Probe 2 are small compared to the pitch of the 2D angle grid, allowing the local slope of the grid profile to be detected. XY displacements are determined independently from value of the local slope because the 2D angle grid has sinusoidal profile in the XY directions. Moreover, θz displacement can be obtained from outputs of Probe 1 and Probe 2. Probe 3, which has larger optical probe than the pitch of the 2D angle grid, can detect the θxθy displacements. The resolution of the developed sensor is 100 nm in the XY directions, 0.01 arcsecond in the θxθy directions and 0.3 arcsecond in the θz direction.
 A surface encoder for 5DOF positin measurement(pdf)
A surface encoder for 5DOF positin measurement(pdf)
 A surface encoder for MDOF position measurement(pdf)
A surface encoder for MDOF position measurement(pdf)
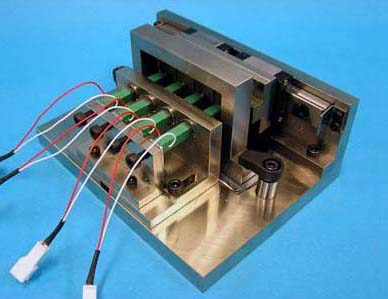
Wave optics-based surface encoder
To consider the influence of phenomena of interference and diffraction generated by shortening the angle grid pitch, the surface encoder model besed on wave-optics is constructed. As a result, it is confirmed that spot on the QPD shows different behavior in 5-degree-of freedom motions, which are the X- and Y-movements, tilt motions about the X- and Y-axes and rotation motion about the Z-axis. In addition, a new 5 degree-of-freedom measurement method is also designed based on the analysis results. The resolution of the new sensor is 70 nm in the XY directions within f3.8 mm and 0.3 arcsecond in the θxθy directions within ±30 arcsecond. Although θz displacement cannot be detected due to defect of PD detectors, an another sensor based on the proposed principle has a resolution of 12 arcsecond in the θz direction within ±2000 arcsecond.
 Wave optics-based surface encoder(pdf)
Wave optics-based surface encoder(pdf)
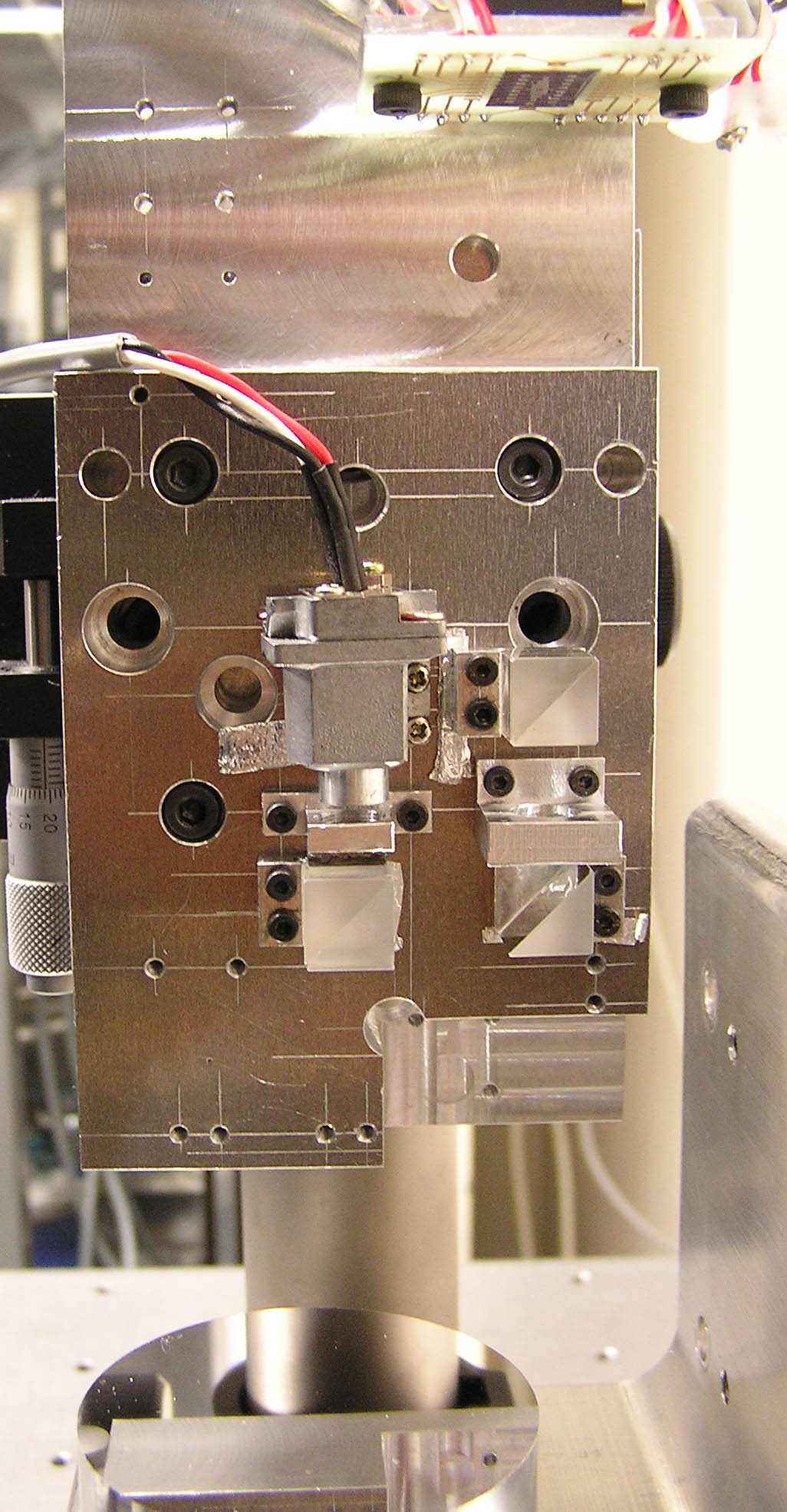
A three-axis displacement sensor with nanometric resolution
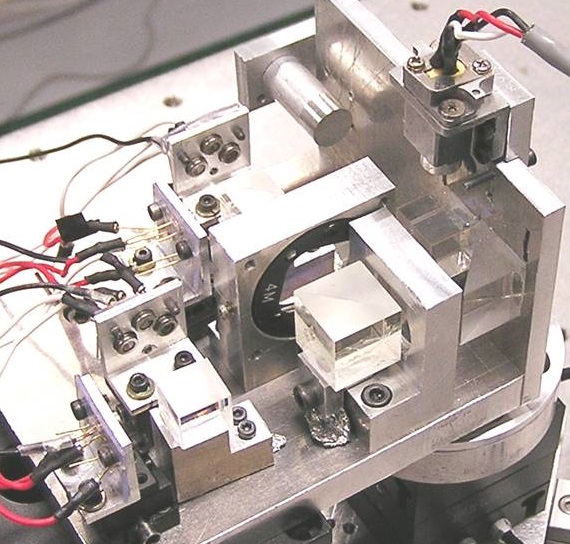
XYZ three-axis measuring system is essential for scanning probe microscopes, optical microscopes, semiconductor manufacturing/inspection machines, laser writing systems, etc. In this research, a new optical sensor for simultaneous detection of XYZ displacements is developed. Displacement in each direction can be calculated from the interference signals, which are generated by diffracted beams from two gratings. Prototype sensor can achieve a resolution of 5 nm in XYZ axes.
Development of a sensitive micro-angle sensor

The sensitivity of an angle sensor based on autocollimation method is propotional to the focal length, so the size of the sensor becomes large to get high-sensitivity. In this research, we propose an micro-angle sensor which employs a laser diode (LD) as a light source and a quadrant photo diode (QPD) as a position sensing device on the focal plane. For developing the high-sensitivity, high-response and 2-axis micro-angle sensor, it is proved that the sensitivity only depends on the incident beam diameter and wavelength and a relationship between the sensitivity and the spot size on the focal plane is simulated. The developed micro-angle sensor has dimensions of 26 × 22.0 × 12.0 mm3, a mass of 0.09 kg, a measurement range of ±30 arcsecond and a resolution of 0.05 arcsecond (5 kHz in frequency bandwidth).
 An angle sensor using a PD array(pdf)
An angle sensor using a PD array(pdf)
 Development of a sensitive micro-angle sensor(pdf)
Development of a sensitive micro-angle sensor(pdf)
Study on nanometrology of aspherical profile

For the purpose of precise profile measurement of micro-aspheric surfaces, we are developing a novel contact-mode scanning probe system available to various profiles and robust to environment. A new algorism is also constructed to measure and compensate the error motions of the scanning stage on-line. In addition, the profile error of the probe sphere, which causes considerable profile measurement errors of micro-aspheric surfaces with large slope variations, is measured and evaluated.
 Study on nanometrology of aspherical profile(pdf)
Study on nanometrology of aspherical profile(pdf)
Slit measurement of slot die

 Slit measurement of slot die(pdf)
Slit measurement of slot die(pdf)
On-machine nanometrology of diamond cutting tools

 On-machine nanometrology of diamond cutting tools(pdf)
On-machine nanometrology of diamond cutting tools(pdf)
A precision AFM probe-unit for measurement of high aspect micro-structured surfaces

 A precision AFM probe-unit for measurement of high aspect micro-structured surfaces(pdf)
A precision AFM probe-unit for measurement of high aspect micro-structured surfaces(pdf)
 A high-precision large area spiral scanning AFM (pdf)
A high-precision large area spiral scanning AFM (pdf)
Replication of a precision 3-D microstructures by UV casting
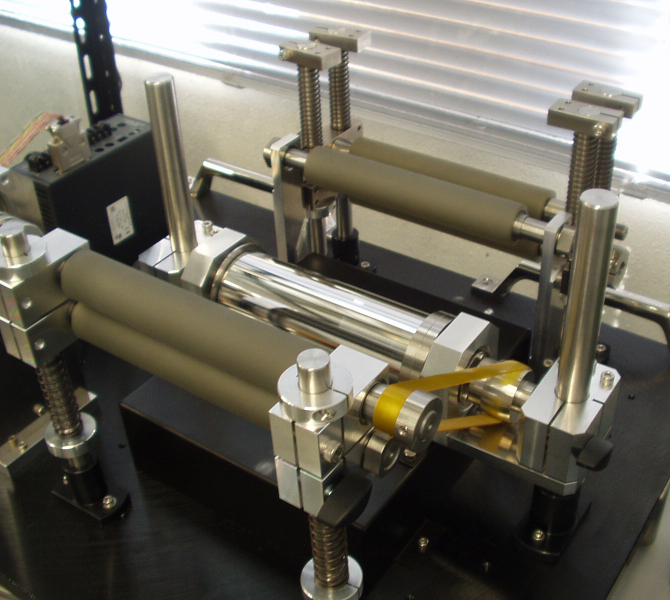

High-accuracy, large-area and high-speed fabrication is important to generate 3-D microstructures utilized as positioning scales. To meet these requirements, replication techniques are developed in this research. A film-type microstructure can be obtained through employing a master roller on which microstructure pattern is generated by ultra precision lathe with assistance of a fast tool servo (FTS). A hot embossing and an UV casting are carried out to replicate the grid surface.
 Replication of a precision 3-D microstructures by UV casting(pdf)
Replication of a precision 3-D microstructures by UV casting(pdf)
Generation of large-area microstructured surface

3D microstructures are widely used in various fields such as positiong scale and micro lens array. The purpose of this research is to generate 3D microstructure on a plate or a roller by diamond turning with an ultra-precision lathe and a fast tool servo (FTS) The fabrication have on the Φ150 mm plate and Φ150 mm ×55 mm roller have been achieved.
 Generation of large-area microstructured surface(pdf)
Generation of large-area microstructured surface(pdf)
 Generation of microstructured pattern to cylinder surface(pdf)
Generation of microstructured pattern to cylinder surface(pdf)
 Fabrication and evaluation of a large-area microstructured cylindrical surface(pdf)
Fabrication and evaluation of a large-area microstructured cylindrical surface(pdf)
Development of a miniaturized fast tool servo

We are reseaching about fabrication of 3D microstructure by single-point diamond turning with an ultra-precision lathe and a fast tool servo (FTS). The FTS is downsized to improve dynamic response and thermal performance. Moreover, high-speed and high accuracy positioning of the FTS is carried out by optimizing the relationship between a piezo-actuator and a driver of it.
 Development of a miniaturized fast tool servo(pdf)
Development of a miniaturized fast tool servo(pdf)