Removal of a lymph node (LN) activates metastatic tumor cells in the lung
2021.06.18 note
Resection of LNs with or without metastasis activates metastatic tumor cells in the lung (mouse experiment).[1-4]
Removal of micrometastatic LNs in breast cancer worsens the prognosis. [5]
Patients: Patients with micrometastases in sentinel lymph nodes
Results of 3-year event-free survival rate (EFS)
patients who had mastectomy EFS: 93.8% vs.
patients who underwent breast-conserving surgery EFS: 97.8%
What is the relationship between the two results?
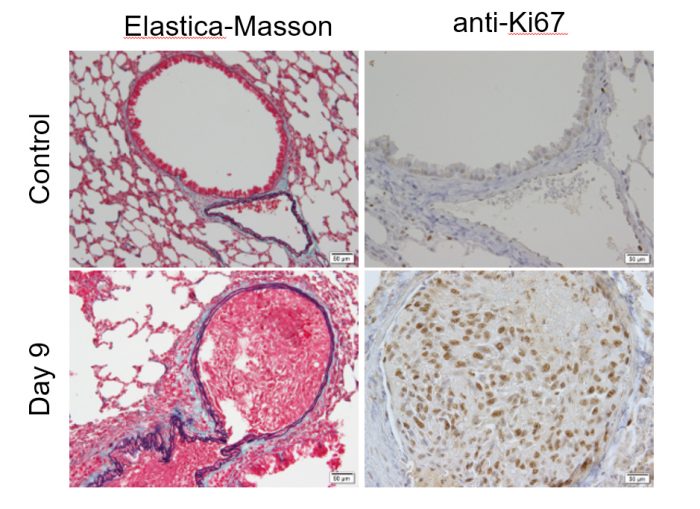
Figure. Metastatic lesion in the lung.
A, B: Control.
C, D: Metastatic lesion in the lung
Metastases were induced in the lungs (day 0).
A Lymph node was removed (day 3).
Metastatic foci were found in the blood vessels of the lung (day 9).
EM: elastic fibers: purple-black, collagen fibers: green, muscle fibers: red Ki67: Cell proliferation marker. Tumor growth is prominent.
References
[1] L. Shao, T. Ouchi, M. Sakamoto, S. Mori, T. Kodama, Activation of latent metastases in the lung after resection of a metastatic lymph node in a lymph node metastasis mouse model, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 460 (2015) 543-548.
[2] A. Sukhbaatar, S. Mori, Y. Saiki, T. Takahashi, A. Horii, T. Kodama, Lymph node resection induces the activation of tumor cells in the lungs, Cancer science, 110 (2019) 509-518.
[3] A. Sukhbaatar, M. Sakamoto, S. Mori, T. Kodama, Analysis of tumor vascularization in a mouse model of metastatic lung cancer, Scientific reports, 9 (2019) 16029.
[4] J. Zheng, L. Jia, S. Mori, T. Kodama, Evaluation of metastatic niches in distant organs after surgical removal of tumor-bearing lymph nodes, BMC cancer, 18 (2018) 608.
[5] A.O. Anderson, N.D. Anderson, Studies on the structure and permeability of the microvasculature in normal rat lymph nodes, Am J Pathol, 80 (1975) 387-418.